“A balance between protection for the artist and rights for the consumer.” – Robin Gross
WHAT IS KNOWN AS COPYRIGHT?
A collection of legal rights vested in your original and authentic creation is known as Copyright. The authors have the right to enjoy financial and other benefits granted by law for their creation. Any such violation of the copyrighted material is considered an infringement of your original creation and is punishable under the Copyright Act. The rationale of the protection is to preserve the copyright content and to reward the general benefits such as the labor of authors on the produced work. These rights include the right to reproduce the work, to prepare derivative works, to distribute copies, and to perform and display the work publicly.
The points to be taken into consideration to get protection from copyright law:-
- Original – A work that is independently created and must not be copied from another source. The quotient of originality varies from one work to another. A work need only demonstrate a very small amount of creativity to meet the originality requirement. Very few creations fail to satisfy the minimum creativity requirement.
- A work of Authorship – A work must be copyrightable i.e. it must be a product of creative expression and idea.
- Tangible Form – A work must be in a fixed and tangible form. It should not merely be an idea in a person’s mind. Instead, the work should be an expression of that idea.
Section 13 of the Indian Copyright Act, 1957 explains what is constituted as Copyrightable material.
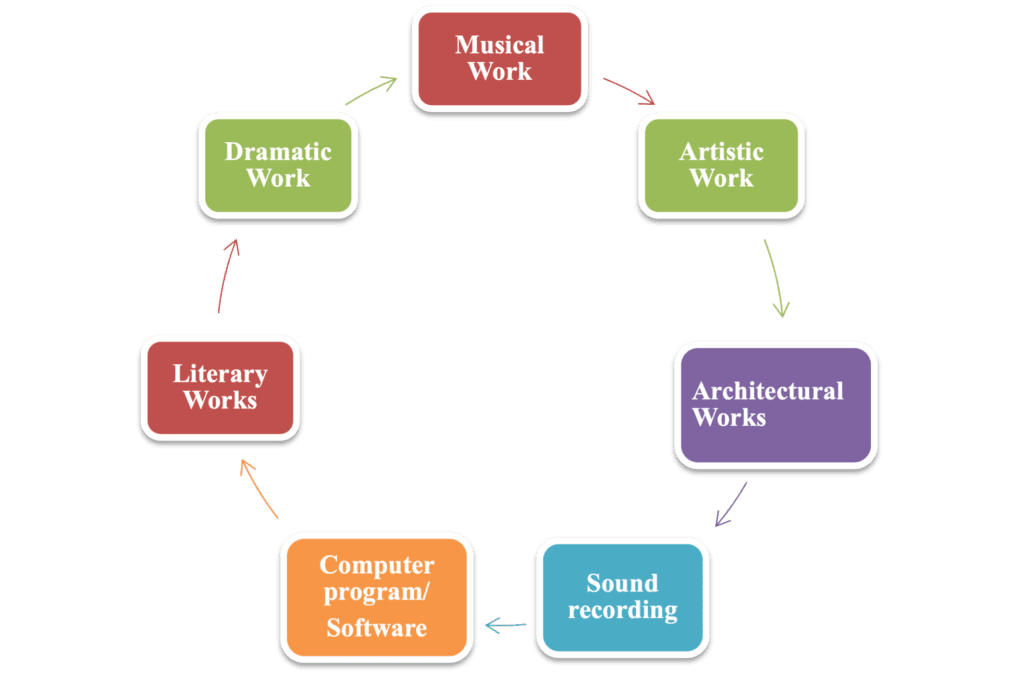
- CATEGORIES OF WORKS THAT IS COPYRIGHTABLE:
- Literary, musical, and dramatic works
- Artistic works
- Choreographic works
- Pictorial, graphic, and sculptural works
- Sound recordings
- Motion pictures and Cinematographic works
- Computer programs and Software
- Compilations of works and derivative works
- Architectural works
- Photographic work
BENEFITS OF COPYRIGHT REGISTRATION
Legal Protection
The act of registration provides shelter to the owner publically. When a work is copyrighted, it is registered on a public record, thereby establishing ownership.
Copyright infringement
In the case of copyright infringement, the authors can sue infringers to secure their work and claim statutory compensation.
Economic Incentive
A copyrighted work helps you reap benefits economically and financially. It also provides an incentive to create more original content.
Transfer of copyright
The rights can be passed or sold for remuneration to a third party by the original copyright holder.
Reputation and Goodwill
By protecting original work, copyright registration ensures that the reputation of their creators/authors is protected. For example, a music composer or author can prevent cheap or duplicate copies of his or her work, thereby preventing any loss of reputation.
PROCEDURE FOR REGISTERING A COPYRIGHT
Creativity being the keystone of progress, no civilized society or prudent man can afford to ignore the basic requirement of encouraging the same. The economic and socio-development of our society is dependent on our creativity and thus copyright provides protection to such creation and efforts of writers, designers, artists, architects, musicians, producers of sound recordings. This creates an atmosphere advantageous to creativity, which encourages them to create more and also motivates others to create. In order to register your original work, you need to register with the Copyright Registrar under Chapter X of the Indian Copyright Act, 1957 and Rule 70 of the Copyright Rules’ 2013.
The steps involved:-
Step 1 – File an Application
An application is needed to be filed either physically in the Copyrights office or through speed/registered post or through the e-filling facility from the official website (copyright.gov.in) by the author of the work, owner of an exclusive right, copyright claimant. A separate application must be filed for registration of each work and a requisite fee is also required to be paid.
Step – 2 Examination
There is a minimum of 30 days waiting period after issuance of the diary number. The waiting period exists so that objections can arise and be reviewed. Further, the process gets divided into two segments:-
- If no objections are raised the examiner will review and scrutinize the applications to find any sort of discrepancy.
- If objections are raised against the Applicant by someone, then letters are sent to both the parties, and they are called to be heard by Registrar.
Step 3 – Registration
This is the final step in which the Registrar might ask for more documents and once satisfied with the copyright claim made by the Applicant; the Registrar of Copyrights would enter details of the copyright into the register of Copyrights and will issue a certificate of registration. Once the process of registration is complete, the Applicant is issued the Extracts of the Register of Copyrights (ROC).
FEES FOR COPYRIGHT FILING
For Literary and Artistic work the Government fee is Rs 500/- per copy.
For detailed Government fee structure, please click at –(https://copyright.gov.in/frmfeedetailsshow.aspx)
The copyright registration process is a lengthy but essential process that might take 10 to 12 months. Thus, it is advisable to register your Copyright in order to protect your moral and economic rights.
For more information, please email – [email protected]

